Anatomy of the Lumbar Spine: A Breakdown
June 28, 2018

Today we end our exploration of the three spinal regions! We’ve covered your cervical and thoracic spines, and last but not least,it’s time to investigate the lumbar. Why is it important? What parts of the body does your lumbar spine actuallyaffect? Let’s take a look!
Today we end our exploration of the three spinal regions! We’ve covered your cervical and thoracic spines, and last but not least, it’s time to investigate the lumbar. Why is it important? What parts of the body does your lumbar spine actually affect? Let’s take a look!
The Importance of Your Lumbar Spine
The lumbar spine is the lowest region of your spine! It’s comprised of five vertebrae in the lower abdomen and hips, and is built for power and stability, bearing the weight of the entire torso and giving the hips and legs the ability to flex and move. It is a strong coat of armor, protecting the base of your spinal cord so it can do its job without interference.
When Your Lumbar Spine is Misaligned
Most people think of the spine in regards to posture, movement and stability, and while those are all important functions, it’s got another crucial role to play—protecting the spinal cord. Messages from the brain travel down the spinal cord, branch out into the nerves and are transmitted to the rest of the body. This is how your organs know how to function and heal.
However, when there’s a misalignment in the vertebrae of the spine, also known as a subluxation, this process is disrupted. And unfortunately, these misalignments can happen at any time; an accident, daily habits and behaviors, nutritional intake, stress and even toxins and chemicals can move your vertebrae out of place.
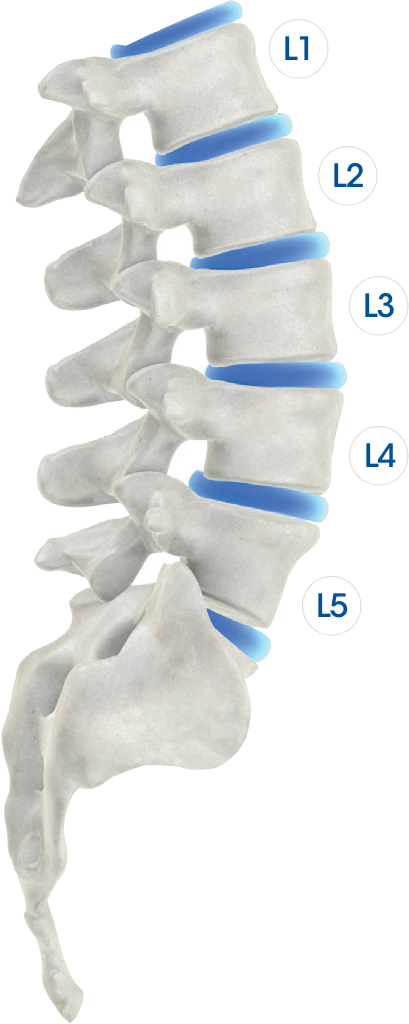
This puts pressure on the spinal nerves and effectively cuts off communication within the nervous system.When left unchecked, these misalignments can affect the body in unexpected ways.Take a look at each vertebra and how it connects with different organs and areas in the body. And most importantly, identify any possible symptoms that could arise from a subluxation in that vertebra!
Lower Back
Lumbar Spine
.cls-1{opacity:0.4;}.cls-2{fill:#eee;}.cls-3,.cls-7{opacity:0.7;}.cls-4{fill:#00a3e6;}.cls-5{fill:#c1261b;}.cls-6{fill:#2f9e3a;}.cls-7,.cls-8{fill:#ffed00;}.cls-8{opacity:0.5;}
| Vertebrae | Parts of the Body | Possible Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| L1 | Large intestines and inguinal rings | Constipation, colitis, dysentery, diarrhea and ruptures or hernias |
| L2 | Appendix, abdomen and upper leg | Cramps, difficulty breathing and minor varicose veins |
| L3 | Sex organs, uterus, bladder and knees | Bladder troubles, painful or irregular periods, miscarriages, bed wetting, impotency and knee pain |
| L4 | Prostate gland, low back muscles and sciatic nerve | Sciatica, lumbago, difficult or painful urination and back aches or pain |
| L5 | Lower legs, ankles and feet | Circulation problems, weak legs, ankles and arches, cold feet and leg cramps |
